Back in 2008, The Atlantic sparked controversy with a provocative cover story: Is Google Making Us Stupid?
In that 4,000-word essay, later expanded into a book, author Nicholas Carr suggested the answer was yes, arguing that technology such as search engines were worsening Americans’ ability to think deeply and retain knowledge.
Wikimedia Foundation
At the core of Carr’s concern was the idea that people no longer needed to remember or learn facts when they could instantly look them up online. While there might be some truth to this, search engines still require users to use critical thinking to interpret and contextualize the results.
Fast-forward to today, and an even more profound technological shift is taking place. With the rise of generative AI tools such as ChatGPT, internet users aren’t just outsourcing memory – they may be outsourcing thinking itself.
Generative AI tools don’t just retrieve information; they can create, analyze and summarize it. This represents a fundamental shift: Arguably, generative AI is the first technology that could replace human thinking and creativity.
That raises a critical question: Is ChatGPT making us stupid?
As a professor of information systems who’s been working with AI for more than two decades, I’ve watched this transformation firsthand. And as many people increasingly delegate cognitive tasks to AI, I think it’s worth considering what exactly we’re gaining and what we are at risk of losing.
AI and the Dunning-Kruger effect
Generative AI is changing how people access and process information. For many, it’s replacing the need to sift through sources, compare viewpoints and wrestle with ambiguity. Instead, AI delivers clear, polished answers within seconds. While those results may or may not be accurate, they are undeniably efficient. This has already led to big changes in how we work and think.
But this convenience may come at a cost. When people rely on AI to complete tasks and think for them, they may be weakening their ability to think critically, solve complex problems and engage deeply with information. Although research on this point is limited, passively consuming AI-generated content may discourage intellectual curiosity, reduce attention spans and create a dependency that limits long-term cognitive development.
To better understand this risk, consider the Dunning-Kruger effect. This is the phenomenon in which people who are the least knowledgeable and competent tend to be the most confident in their abilities, because they don’t know what they don’t know. In contrast, more competent people tend to be less confident. This is often because they can recognize the complexities they have yet to master.
This framework can be applied to generative AI use. Some users may rely heavily on tools such as ChatGPT to replace their cognitive effort, while others use it to enhance their capabilities. In the former case, they may mistakenly believe they understand a topic because they can repeat AI-generated content. In this way, AI can artificially inflate one’s perceived intelligence while actually reducing cognitive effort.
This creates a divide in how people use AI. Some remain stuck on the “peak of Mount Stupid,” using AI as a substitute for creativity and thinking. Others use it to enhance their existing cognitive capabilities.
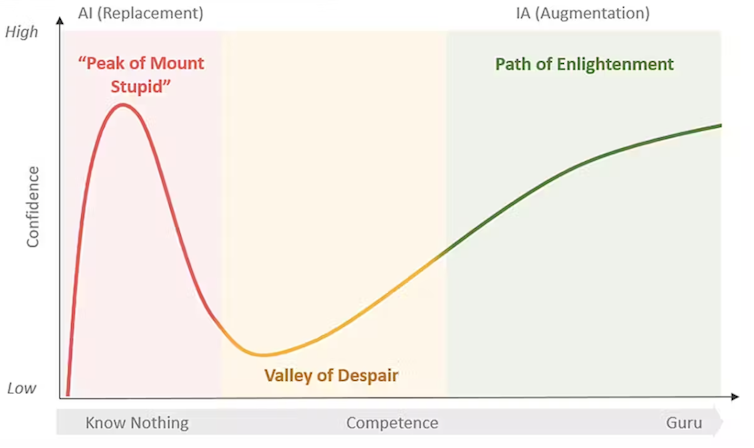
This image illustrates the journey from overconfidence in AI as a substitute for thinking (the Peak of Mount Stupid) through disillusionment and toward true value creation. From ‘Artificial Intelligence to Augmented Intelligence: A Shift in Perspective, Application, and Conceptualization of AI’ (2024) by Aaron French and J.P. Shim.
In other words, what matters isn’t whether a person uses generative AI, but how. If used uncritically, ChatGPT can lead to intellectual complacency. Users may accept its output without questioning assumptions, seeking alternative viewpoints or conducting deeper analysis. But when used as an aid, it can become a powerful tool for stimulating curiosity, generating ideas, clarifying complex topics and provoking intellectual dialogue.
The difference between ChatGPT making us stupid or enhancing our capabilities rests in how we use it. Generative AI should be used to augment human intelligence, not replace it. That means using ChatGPT to support inquiry, not to shortcut it. It means treating AI responses as the beginning of thought, not the end.
AI, thinking and the future of work
The mass adoption of generative AI, led by the explosive rise of ChatGPT – it reached 100 million users within two months of its release – has, in my view, left internet users at a crossroads. One path leads to intellectual decline: a world where we let AI do the thinking for us. The other offers an opportunity: to expand our brainpower by working in tandem with AI, leveraging its power to enhance our own.
It’s often said that AI won’t take your job, but someone using AI will. But it seems clear to me that people who use AI to replace their own cognitive abilities will be stuck at the peak of Mount Stupid. These AI users will be the easiest to replace.
It’s those who take the augmented approach to AI use who will reach the path of enlightenment, working together with AI to produce results that neither is capable of producing alone. This is where the future of work will eventually go.
This essay started with the question of whether ChatGPT will make us stupid, but I’d like to end with a different question: How will we use ChatGPT to make us smarter? The answers to both questions depend not on the tool but on users.

The post “Is ChatGPT making us stupid?” by Aaron French, Assistant Professor of Information Systems, Kennesaw State University was published on 07/24/2025 by theconversation.com