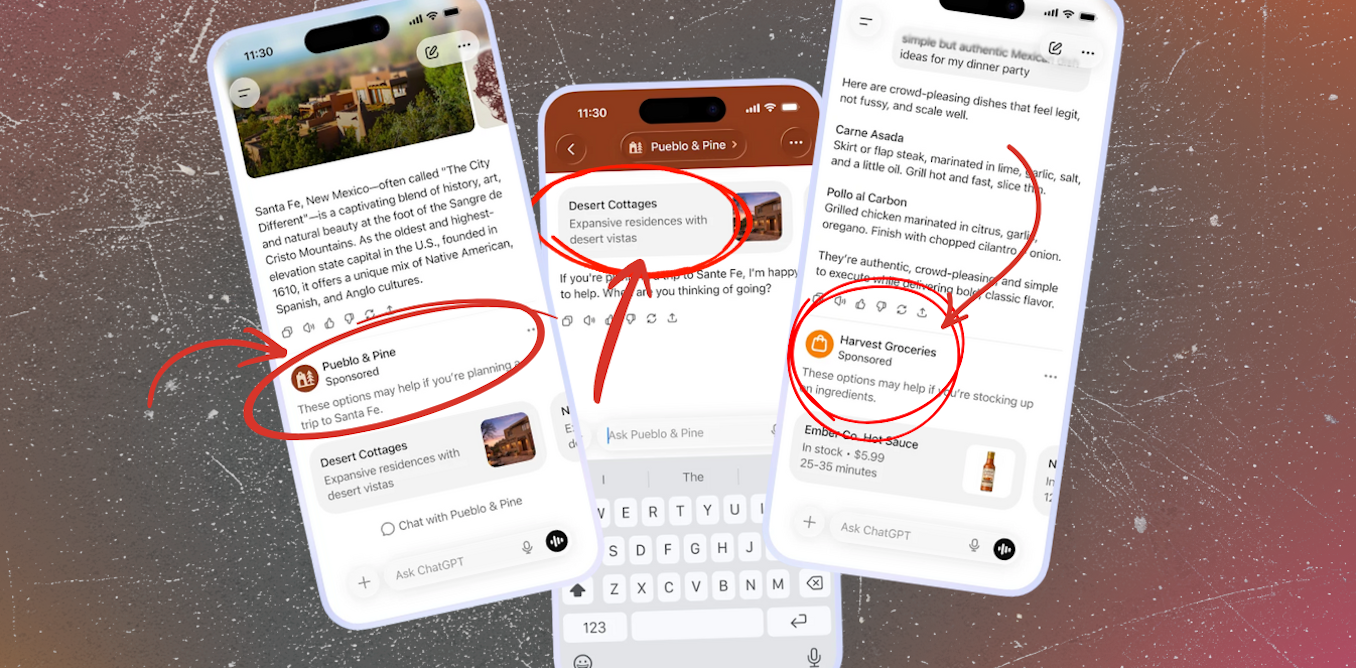
OpenAI has announced plans to introduce advertising in ChatGPT in the United States. Ads will appear on the free version and the low-cost Go tier, but not for Pro, Business, or Enterprise subscribers.
The company says ads will be clearly separated from chatbot responses and will not influence outputs. It has also pledged not to sell user conversations, to let users turn off personalised ads, and to avoid ads for users under 18 or around sensitive topics such as health and politics.
Still, the move has raised concerns among some users. The key question is whether OpenAI’s voluntary safeguards will hold once advertising becomes central to its business.
Why ads in AI were always likely
We’ve seen this before. Fifteen years ago, social media platforms struggled to turn vast audiences into profit.
The breakthrough came with targeted advertising: tailoring ads to what users search for, click on, and pay attention to. This model became the dominant revenue source for Google and Facebook, reshaping their services so they maximised user engagement.
Read more:
Why is the internet overflowing with rubbish ads – and what can we do about it?
Large-scale artificial intelligence (AI) is extremely expensive. Training and running advanced models requires vast data centres, specialised chips, and constant engineering. Despite rapid user growth, many AI firms still operate at a loss. OpenAI alone expects to burn US$115 billion over the next five years.
Only a few companies can absorb these costs. For most AI providers, a scalable revenue model is urgent and targeted advertising is the obvious answer. It remains the most reliable way to profit from large audiences.
What history teaches us about OpenAI’s promises
OpenAI says it will keep ads separate from answers and protect user privacy. These assurances may sound comforting, but, for now, they rest on vague and easily reinterpreted commitments.
The company proposes not to show ads “near sensitive or regulated topics like health, mental health or politics”, yet offers little clarity about what counts as “sensitive,” how broadly “health” will be defined, or who decides where the boundaries lie.
Most real-world conversations with AI will sit outside these narrow categories. So far OpenAI has not provided any details on which advertising categories will be included or excluded. However, if no restrictions were placed on the content of the ads, it’s easy to picture that a user asking “how to wind down after a stressful day” might be shown alcohol delivery ads. A query about “fun weekend ideas” could surface gambling promotions.
These products are linked to recognised health and social harms. Placed beside personalised guidance at the moment of decision-making, such ads can steer behaviour in subtle but powerful ways, even when no explicit health issue is discussed.
Similar promises about guardrails marked the early years of social media. History shows how self-regulation weakens under commercial pressure, ultimately benefiting companies while leaving users exposed to harm.
Advertising incentives have a long record of undermining the public interest. The Cambridge Analytica scandal exposed how personal data collected for ads could be repurposed for political influence. The “Facebook files” revealed that Meta knew its platforms were causing serious harms, including to teenage mental health, but resisted changes that threatened advertising revenue.
More recent investigations show Meta continues to generate revenue from scam and fraudulent ads even after being warned about their harms.
Why chatbots raise the stakes
Chatbots are not merely another social media feed. People use them in intimate, personal ways for advice, emotional support and private reflection. These interactions feel discreet and non-judgmental, and often prompt disclosures people would not make publicly.
That trust amplifies persuasion in ways social media does not. People seek help and make decisions when they consult chatbots. Even with formal separation from responses, ads appear in a private, conversational setting rather than a public feed.
Messages placed beside personalised guidance – about products, lifestyle choices, finances or politics – are likely to be more influential than the same ads seen while browsing.
As OpenAI positions ChatGPT as a “super assistant” for everything from finances to health, the line between advice and persuasion blurs.
For scammers and autocrats, the appeal of a more powerful propaganda tool is clear. For AI providers, the financial incentives to accommodate them will be hard to resist.
The root problem is a structural conflict of interest. Advertising models reward platforms for maximising engagement, yet the content that best sustains attention is often misleading, emotionally charged or harmful to health.
This is why voluntary restraint by online platforms has repeatedly failed.
Is there a better way forward?
One option is to treat AI as digital public infrastructure: these are essential systems designed to serve the public rather than maximise advertising revenue.
This need not exclude private firms. It requires at least one high-quality public option, democratically overseen – akin to public broadcasters alongside commercial media.
Elements of this model already exist. Switzerland developed the publicly funded AI system Apertus through its universities and national supercomputing centre. It is open source, compliant with European AI law, and free from advertising.
Australia could go further. Alongside building our own AI tools, regulators could impose clear rules on commercial providers: mandating transparency, banning health-harming or political advertising, and enforcing penalties – including shutdowns – for serious breaches.
Advertising did not corrupt social media overnight. It slowly changed incentives until public harm became the collateral damage of private profit. Bringing it into conversational AI risks repeating the mistake, this time in systems people trust far more deeply.
The key question is not technical but political: should AI serve the public, or advertisers and investors?
The post “OpenAI will put ads in ChatGPT. This opens a new door for dangerous influence” by Raffaele F Ciriello, Senior Lecturer in Business Information Systems, University of Sydney was published on 01/23/2026 by theconversation.com














.jpg)