The era of AI-assisted online violence is no longer looming. It has arrived. And it is reshaping the threat landscape for women who work in the public sphere around the world.
Our newly published report commissioned by UN Women offers early, urgent evidence indicating that generative AI is already being used to silence and harass women whose voices are vital to the preservation of democracy.
This includes journalists exposing corruption, activists mobilising voters and the human rights defenders working on the frontline of efforts to stall democratic backsliding.
Based on a global survey of women human rights defenders, activists, journalists and other public communicators from 119 countries, our research shows the extent to which generative AI is being weaponised to produce abusive content – in a multitude of forms – at scale.
We surveyed 641 women in five languages (Arabic, English, French, Portuguese and Spanish). The surveys were disseminated via the trusted networks of UN Women, Unesco, the International Center for Journalists and a panel of 22 expert advisers representing intergovernmental organisations, the legal fraternity, civil society organisations, industry and academia.
According to our analysis, nearly one in four (24%) of the 70% of respondents who reported experiencing online violence in the course of their work identified abuse that was generated or amplified by AI tools. In the report, we define online violence as any act involving digital tools which results in or is likely to result in physical, sexual, psychological, social, political or economic harm, or other infringements of rights and freedoms.
But the incidence is not evenly distributed across professions. Women who identify as writers or other public communicators, such as social media influencers, reported the highest exposure to AI-assisted online violence at 30.3%. Women human rights defenders and activists followed closely at 28.2%. Women journalists and media workers reported a still alarming 19.4% exposure rate.
Since the public launch of free, widely accessible generative AI tools such as ChatGPT at the end of 2022, the barriers to entry and cost of producing sexually explicit deepfake videos, gendered disinformation, and other forms of gender-based online violence have been significantly reduced. Meanwhile, the speed of distribution has intensified.
The result is a digital landscape in which harmful, misogynistic content can be generated rapidly by anyone with a smart phone and access to a generative AI chatbot. Social media algorithms, meanwhile, are tuned to boost the reach of the hateful and abusive material, which then proliferates. And it can generate considerable personal, political and often financial gains for the perpetrators and facilitators, including technology companies.
Meanwhile, recent research highlights AI both as a driver of disinformation and as a potential solution, powering synthetic content detection systems and counter-measures. But there’s limited evidence of how effective these detection tools are.
Many jurisdictions also still lack clear legal frameworks that address deepfake abuse and other harms enabled by AI-generated media, such as financial scams and digital impersonation. This is especially the case when the attack is gendered, rather than purely political or financial. This is due to the inherently nuanced and often insidious nature of misogynistic hate speech, along with the evident indifference of lawmakers to women’s suffering.
Our findings underscore an urgent two-fold challenge. There’s a desperate need for stronger tools to identify, monitor, report and repel AI-assisted attacks. And legal and regulatory mechanisms must be established that require platforms and AI developers to prevent their technologies from being deployed to undermine women’s rights.
When online abuse leads to ‘real-world’ attacks
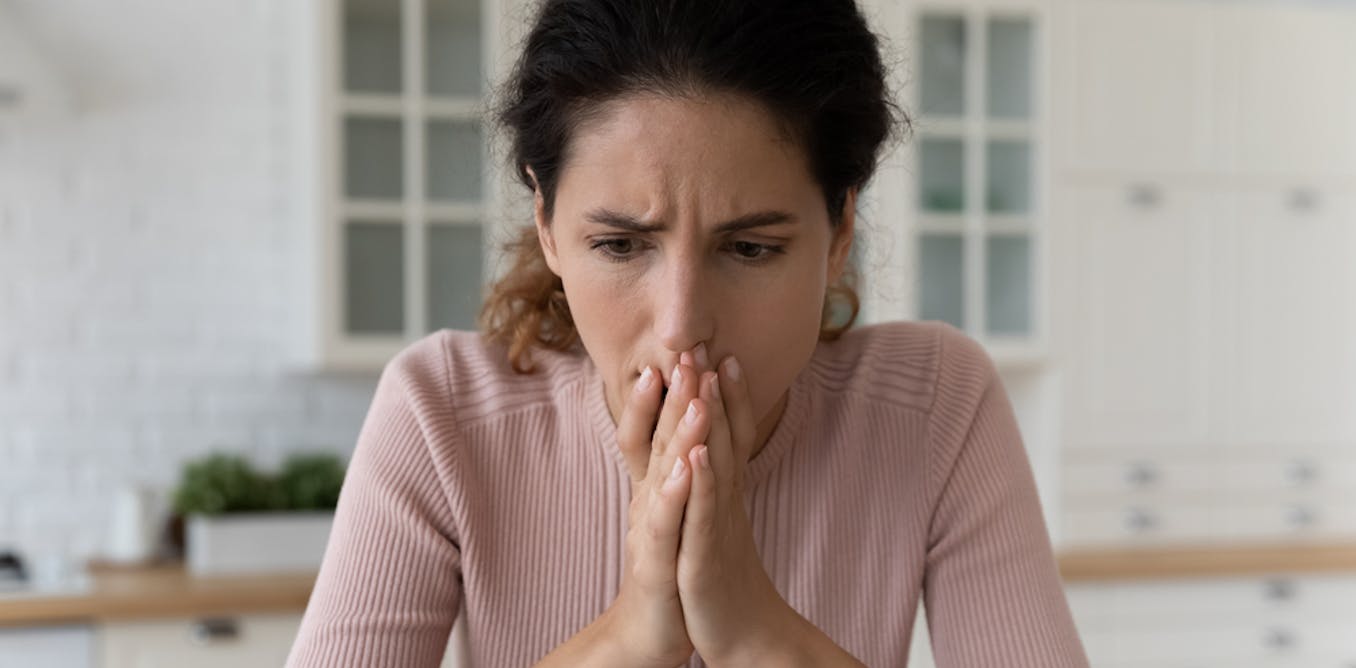
We can’t treat these AI-related findings as isolated statistics. They exist amid broadening online violence against women in public life. They are also situated within a wider and deeply unsettling pattern – the vanishing boundary between online violence and offline harm.
Four in ten (40.9%) women we surveyed reported experiencing offline attacks, abuse or harassment that they linked to online violence. This includes physical assault, stalking, swatting and verbal harassment. The data confirms what survivors have been telling us for years: digital violence is not “virtual” at all. In fact, it is often only the first act in a cycle of escalating harm.
EPA/Christopher Neundorf
For women journalists, the trend is especially stark. In a comparable 2020 survey, 20% of respondents reported experiencing offline attacks associated with online violence. But five years later, that figure has more than doubled to 42%. This dangerous trajectory should be a wake-up call for news organisations, governments and big tech companies alike.
When online violence becomes a pathway to physical intimidation, the chilling effect extends far beyond individual targets. It becomes a structural threat to freedom of expression and democracy.
In the context of rising authoritarianism, where online violence and networked misogyny are typical features of the playbook for rolling back democracy, the role of politicians in perpetrating online violence cannot be ignored. In the 2020 Unesco-published survey of women journalists, 37% of respondents identified politicians and public office holders as the most common offenders.
The situation has only deteriorated since 2020, with the evolution of a continuum of violence against women in the public sphere. Offline abuse, such as politicians and pubic office holders targeting female journalists during media conferences, can trigger an escalation of online violence that, in turn, can exacerbate offline harm.
This cycle has been documented all over the world, in the stories of notable women journalists like Maria Ressa in the Philippines, Rana Ayyub in India and the assassinated Maltese investigative jouralist Daphne Caruana Galizia. These women bravely spoke truth to power and were targeted by their respective governments – online and offline – as a result.
The evidence of abuse against women in public life we have uncovered during our research signals a need for more creative technological interventions employing the principles of “human rights by design”. These are safeguards recommended by a range of international organisations which build in protections for human rights at every stage of AI design. It also signals the need for stronger and more proactive legal and policy responses, greater platform accountability, political responsibility, and better safety and support systems for women in public life.

The post “AI tools are being used to subject women in public life to online violence” by Julie Posetti, Director of the Information Integrity Initiative, a project of TheNerve/Professor of Journalism, Chair of the Centre for Journalism and Democracy, City St George’s, University of London was published on 12/17/2025 by theconversation.com











.jpg)